
Leave Your Message

When it comes to lifting heavy loads, the choice of crane ropes is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency. As we look toward 2025, understanding the different types of crane ropes available on the market can make a significant difference in the performance of lifting operations. Whether you are operating in construction, shipping, or manufacturing, selecting the right material and design for crane ropes can enhance not only the durability and strength of your equipment but also contribute to smoother operations and reduced downtime.
In this essential guide, we will delve into the various types of crane ropes, highlight their specific characteristics, and discuss the key factors to consider when making an informed choice. From synthetic fibers to steel cables, each type of crane rope has its own advantages and disadvantages, and knowing these can help you tailor your selection to your unique operational needs. Whether you are upgrading existing equipment or investing in new machinery, understanding crane ropes is an indispensable aspect of maximizing your lifting capabilities and ensuring the safety of your workforce.

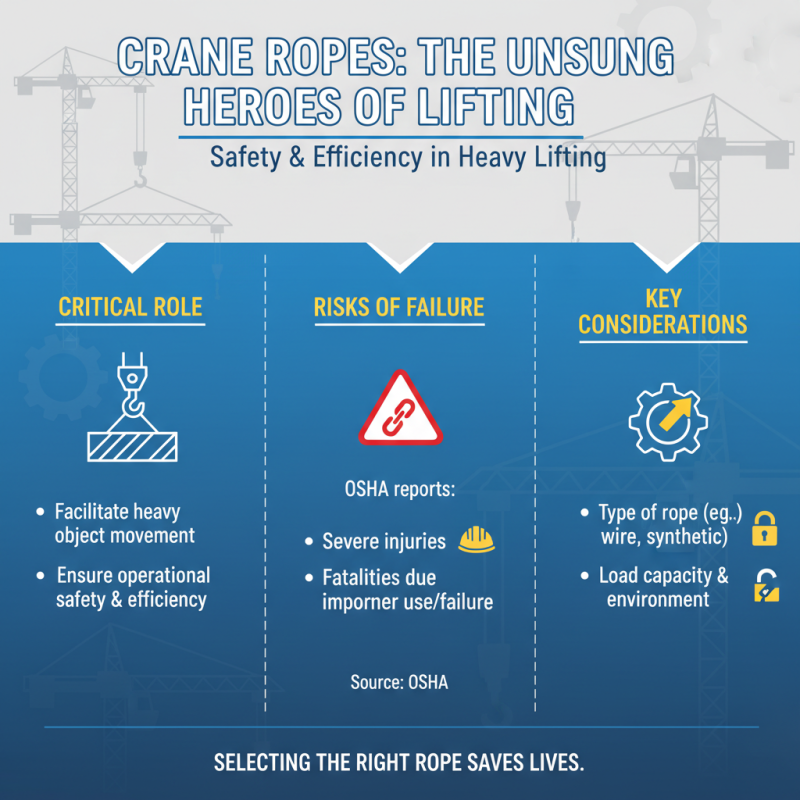
Crane ropes play a critical role in lifting operations across various industries, from construction to manufacturing. They are essential for ensuring the safety and efficiency of heavy lifting tasks. According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), improper use or failure of crane ropes can lead to accidents resulting in severe injuries or fatalities. This underscores the importance of selecting the right type of crane rope based on the specific operational needs and environmental conditions.
Lifting operations often require different types of crane ropes, including wire ropes and synthetic ropes. Wire ropes are known for their high tensile strength and durability, making them suitable for heavy loads. For instance, a report from the International Crane Stakeholders Assembly suggests that wire ropes can support loads exceeding 100 tons, depending on their diameter and construction. On the other hand, synthetic ropes are lightweight and offer flexibility, making them ideal for applications where weight and maneuverability are critical. Data indicates that synthetic ropes can reduce the overall weight of the lifting equipment by up to 60%, which can lead to enhanced productivity and reduced wear on hoisting mechanisms.
Understanding the distinct characteristics and applications of crane ropes allows operators to make informed decisions, optimizing both safety and operational efficiency. Proper maintenance and periodic inspections are also vital, as the lifespan of crane ropes can significantly influence the reliability of lifting operations. Regular assessments can identify wear and tear, helping to prevent failures that could lead to operational downtime or accidents.
When selecting crane ropes, understanding the various materials and their associated strength characteristics is crucial. Crane ropes are typically made from steel, synthetic fibers, or a combination of both. Steel ropes are favored for their superior tensile strength and resilience. According to industry reports, steel wire ropes can withstand loads ranging from 1,000 to over 200,000 pounds, depending on their diameter and construction. This makes them suitable for heavy lifting applications in construction and shipping sectors.
On the other hand, synthetic ropes, such as those made from polyester or nylon, offer excellent flexibility and are lightweight, which can be beneficial in specific scenarios. For example, polyamide ropes can provide a break strength of up to 27,000 pounds while being significantly lighter than steel alternatives. However, they may not be suitable for high-temperature applications due to their lower heat resistance.
**Tips:** When choosing a crane rope, consider the type of load and the lifting environment. Always consult the manufacturer's specifications for load ratings, and perform regular inspections to ensure rope integrity. Additionally, keep in mind that regular maintenance, such as keeping synthetic ropes clean and dry, extends their life and performance.
In conclusion, understanding the trade-offs between steel and synthetic crane ropes can guide you in making an informed choice based on specific project needs. Selecting the appropriate rope type can enhance safety and efficiency in any lifting operation.
When selecting crane ropes for specific projects, several key factors must be considered to ensure safety, efficiency, and longevity. One of the foremost considerations is the type of material used in the rope. Common materials include steel and synthetic options, each with unique benefits. Steel ropes are known for their strength and durability, making them ideal for heavy loads and rough environments. In contrast, synthetic ropes are lighter and often have better resistance to environmental factors, such as UV rays and chemicals, which can be crucial for outdoor projects.
Another critical aspect is the rope's diameter and construction. The diameter affects the rope's load capacity and flexibility, which can significantly impact maneuverability in tight spaces. Additionally, different constructions, such as lay patterns, can influence the rope's performance under various conditions. For example, a right-hand lay rope may twist differently than a left-hand lay, impacting how it is handled during use. Therefore, understanding the specific demands of the project, including load requirements, environmental conditions, and handling practices, is essential in selecting the right crane rope for optimal results.
When it comes to crane ropes, maintenance and safety are paramount for ensuring longevity and reliability. According to a recent industry report from the International Association of Crane and Rigging Professionals, improper maintenance accounts for over 20% of crane-related incidents. Regular inspection of crane ropes is critical; operators should check for signs of wear, such as fraying or corrosion, at least once a month. Additionally, the usage of wire ropes should be documented, as tracking their operational history can help identify patterns in wear and prevent catastrophic failures.
Proper lubrication is equally essential in extending the life of crane ropes. A study published in the Journal of Construction Engineering and Management highlights that well-lubricated ropes can last up to 30% longer than those that are not maintained. Operators should utilize the appropriate type of lubricant based on the rope's material and environmental conditions. Furthermore, adhering to safe load limits, as specified in operational guidelines, is crucial; overloading can severely compromise the integrity of crane ropes, leading to unexpected failures and potential accidents. By following these maintenance practices, operators can significantly enhance the performance and durability of crane ropes.
As we look towards the future of crane rope technology, significant trends are reshaping the landscape. Innovations in material science, such as the development of high-performance synthetic fibers, are enhancing the durability and strength of crane ropes. These advancements not only improve the overall performance of crane operations but also contribute to greater safety standards. The shift towards lightweight yet robust materials means that cranes can lift heavier loads more efficiently, reducing fuel consumption and operational costs.
When selecting the right type of crane rope, consider the specific requirements of your projects. Lighter materials may provide better handling and increased load capacity, but it's crucial to assess their suitability for your working environment. Examine the rope construction as well; multi-strand designs can offer enhanced flexibility and resistance to wear.
Tips: Always inspect your crane ropes regularly for signs of wear and tear. Additionally, educate your team about the latest advancements in crane rope technology to ensure they are using the most efficient and safe options available. Staying informed about industry trends can lead to better investment decisions and improved operational efficiency in the long run.
| Rope Type | Material | Diameter (mm) | Weight (kg/m) | Breaking Strength (kN) | Applications | Future Trends |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel Wire Rope | Steel | 20 | 1.25 | 200 | Construction, Shipbuilding | High performance coatings |
| Synthetic Rope | Polyester | 18 | 0.85 | 150 | Marine, Cranes | Lightweight and buoyant |
| High Tenacity Rope | Nylon | 25 | 1.70 | 250 | Heavy Lifting, Logging | Enhanced abrasion resistance |
| Multi-strand Rope | Steel | 22 | 1.45 | 220 | Mining, Dredging | Improved flexibility and fatigue resistance |
| Compacted Rope | Aluminum | 15 | 0.50 | 100 | Industrial Cranes | Corrosion-resistant design |





